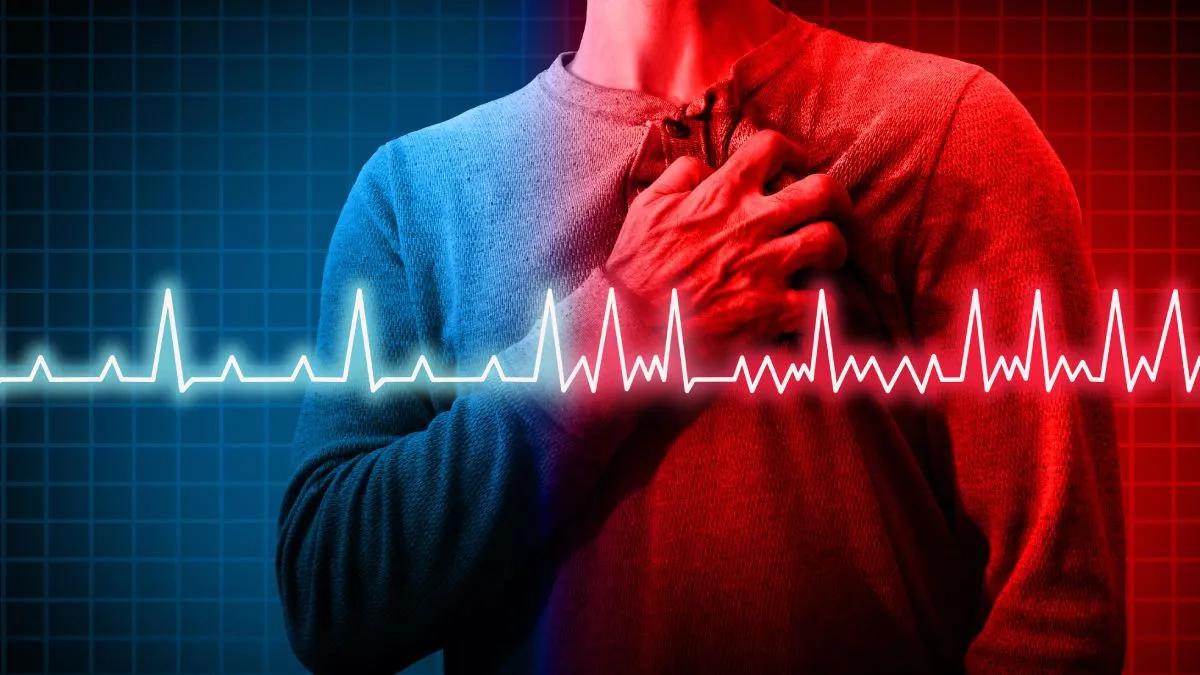
People who suffer a myocardial infarction at a young age have two preventable risk factors to a large extent.This was revealed in a study presented at the Spanish Society of Cardiology, and could be the key to preventing the disease in young people.
Premature heart attack.These are risk factors in young patients
This article has been prepared and reviewed to meet the most stringent data and quality standards.It is based on scientific studies that have a self-healing process from the Journal of Self-Health, reliable sources that are the opinion of the leaders of the Society of Science, Professional Associations, Universities and prestigious Hospitals among others.You will find the information below in the Bibliography and other sources linked in the text.More information
There are two things that prevent people from suffering from a fake Myocardial infarction.This was determined by a study presented at the Congress of the Spanish Society of Cardiology, which provides the keys to prevent this disease in young people.
Update on: Friday, October 24, 2025 10:00:00 ctiver m myicard when carls the most popular things still agree to agree.
This can be seen from the ocrulysis of the "Genomi-prophylaxis" research institute held by the National Congress of "Grandiologists" held by the National Congress of "Grandiologists" from October 20 to 25.Early, namely a heart attack before the age of 55 years and in women occurs from the age of 65 years.Early heart attacks of all cases represent almost one third.
According to experts, smoking and changes in cholesterol levels are the two main factors of heart attack."Patients with early ischemic heart disease showed significant clinical differences compared to those who developed later," he pointed out.Coronary artery disease."
In particular, 47.4% of patients with a first heart attack, compared to others suffering from heart disease, are attacked by an old disease.The same thing happens with diabetes: it was only seen in patients with a heart attack who had a heart attack, compared to those who had a heart attack later.
However, there was a higher proportion of active smokers (60% vs 29%) and more frequent coronary heart disease (17.8% vs 11.2%) or hypercholesterolemia or high cholesterol or a family history of high cholesterol (13.6% vs 7.8%).
These results can be seen, according to Bunono, "The need to continue working in the affected areas, and promote tobacco restrictions, including smoking, healthy eating and physical activity."
Differentiation factors in women
Genome-prevalence studies also show that men and women have different risk profiles.Bueno's exception is basically not only the traditional risk factors, that is, not only the floating risk factors, that is, the floating.They are closely related to education, cultural level, anxiety, worry, anxiety or depression, among other elements.
For example, "the overall level of education as well as the economic, labor and wage situation is worse for women than for men."In addition, women shoulder a greater burden of unpaid work, including childcare, elder care and housework, which are "associated with higher levels of anxiety and depression."The cardiologist said the prevalence of anxiety and depression in women was "about twice that of men".Today, "depression is known to be virtually identical to traditional cardiovascular risk factors," he adds.
According to Buono, women's disproportionate burden of care and work is still not being talked about enough - and strong action is not being taken.Heart attacks in young adults are caused by an accumulation of risk factors such as genetics, cholesterol, smoking and high blood pressure. But in the case of women, we must include other factors that have not been given enough attention.
According to cardiology, demographic changes contribute to the onset of delayed heart disease.In fact, he noted, "the rate is declining in both men and women." However, while the rate continues to decline at a faster rate, among women, no such structure is seen, but rather "a structure that has already developed."
Advances in the treatment of heart disease have contributed to reducing the death rate due to this cause. But according to the latest data from the National Institute of Statistics, this number is due to "death" in the community, which includes heart disease and stroke. Most of the deaths occurred in 2024, with 26,851 deaths, 3.2 percent lower than in 2023.